Industries are constantly seeking ways to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance safety, slowly but safely catching up with automation generation. One technology that stands out is the Automated Guided Vehicle (AGV). But what exactly is an AGV? How does it work and transform modern operations? In this article, Phenikaa-X will guide you deep into the world of AGV, exploring their applications, types, benefits, and the cutting-edge technology that makes them special.
1. What Are Automated Guided Vehicles?
An AGV, or Automated Guided Vehicle/Automatic Guided Vehicle – referred as AGV robot or robot AGV, is a driverless, self-guided robot designed to transport materials, products, or tools within a facility without human intervention. These vehicles follow predefined paths or use advanced navigation systems to move efficiently. Unlike traditional vehicles, AGVs don’t require an onboard operator, making them a cornerstone of AGV automation in industries like manufacturing, warehousing and logistics.

With that being said, AGV robots can operate autonomously, eliminating the need for an operator. This autonomy makes them being considered the “Future of automation technology”, a field that integrates robotics, software, and sensors to optimize industrial processes.
In real action, the AGV robots can perform a variety of tasks. For example, they can pick up heavy loads from one location, transport them across the facility, and deliver them to a designated spot – all while avoiding obstacles and coordinating with other equipment. Some AGVs are even capable of collaborating with human workers or other machines, making them highly adaptable to dynamic environments.
The concept of AGVs dates back to the 1950s when the first rudimentary models were introduced in factories to tow materials along fixed paths. Since then, AGVs have evolved dramatically, incorporating cutting-edge innovations such as artificial intelligence (AI), laser navigation and real-time data processing.
Today, they are a vital component of industries like warehousing, logistics, even start showing in healthcare and E-commerce, proving that AGVs are far more than just a passing trend – they’re a fundamental shift in how humans approach material handling.
2. AGV Applications
The versatility of AGV robots is one of their greatest strengths, allowing them to serve a wide array of industries and applications. Below are some of the most prominent applications of AGV automated guided vehicles:
-
Warehousing
AGV automated guided vehicles are capable of optimizing inventory management and streamlining operations. These vehicles can move goods between storage racks, loading docks and picking stations with remarkable speed while maintain high accuracy.
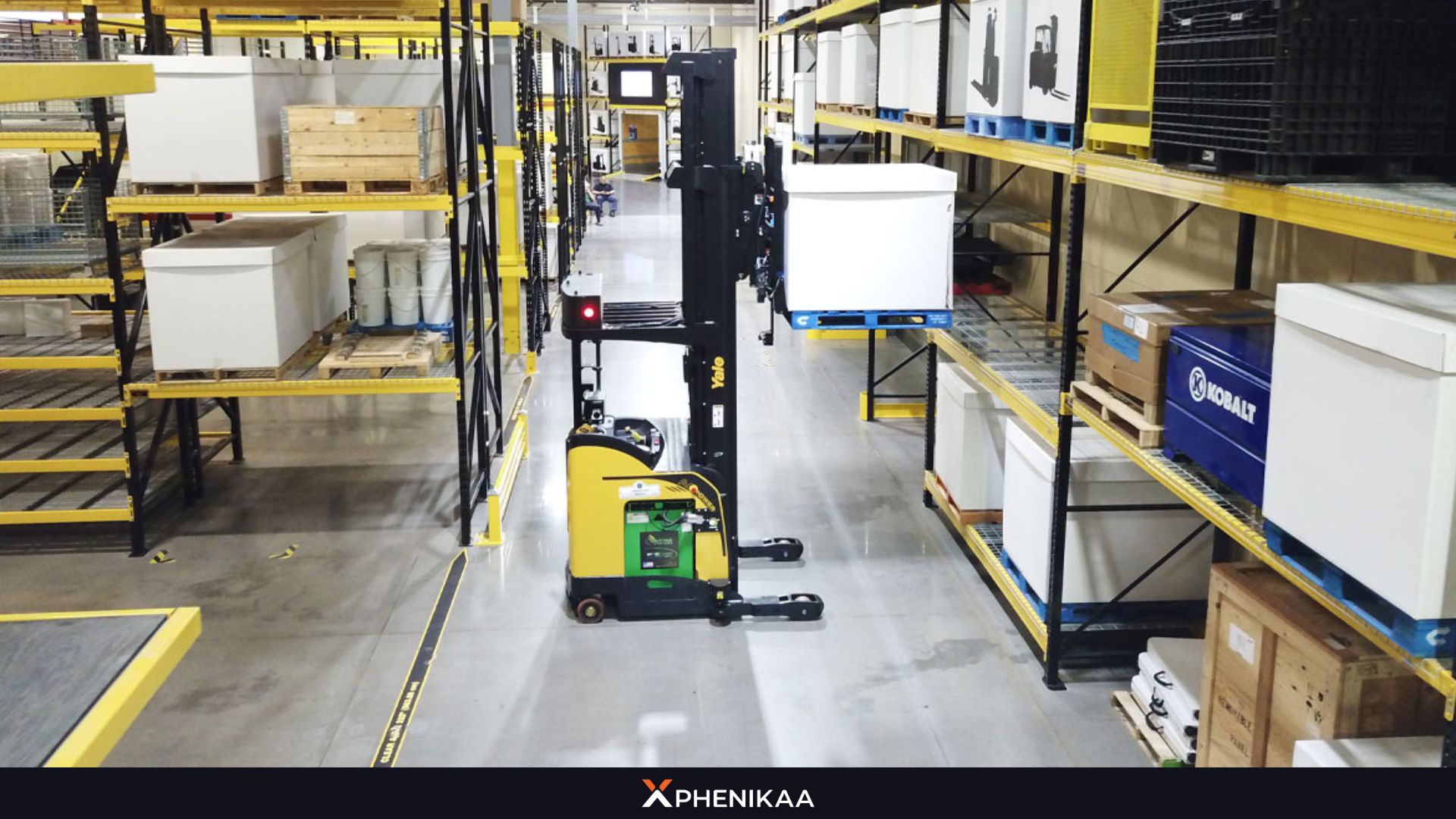

This reduces the time workers spend on repetitive tasks and ensures that inventory is handled efficiently. Furthermore, AGVs can integrate with warehouse management systems (WMS) to provide real-time updates on stock levels and locations, enhancing overall operational visibility.
-
Manufacturing
Manufacturing facilities in recent years begin to rely heavily on AGV to transport raw materials, components, and finished products along assembly lines. These robots can replace workers to carry engine parts from a supply area to a production station, then transport the assembled engine to the next stage of the process.
This seamless flow of materials minimizes bottlenecks, reduces downtime, and ensures that production schedules are met, avoiding excess inventory and waste. AGV in manufacturing bring many benefits interm of cost, efficiency, safety,… which make them being used widely and cosidered the “future of manufacturing”.
-
Healthcare
In healthcare settings, AGV Robot is still new to this industry. Commonly they are used to deliver medical supplies, meals, linens, or even hazardous waste, reducing the need for staff to perform time-consuming logistical tasks.
Although they are all simple tasks, AGV support allows healthcare personnel to focus on patient care rather than material handling.
-
E-commerce
The explosive growth of online shopping has placed immense pressure on e-commerce companies to fulfill orders quickly and accurately. In this field, AGV Robot plays a key role in fulfillment centers by moving packages between storage areas, sorting stations, and shipping docks.
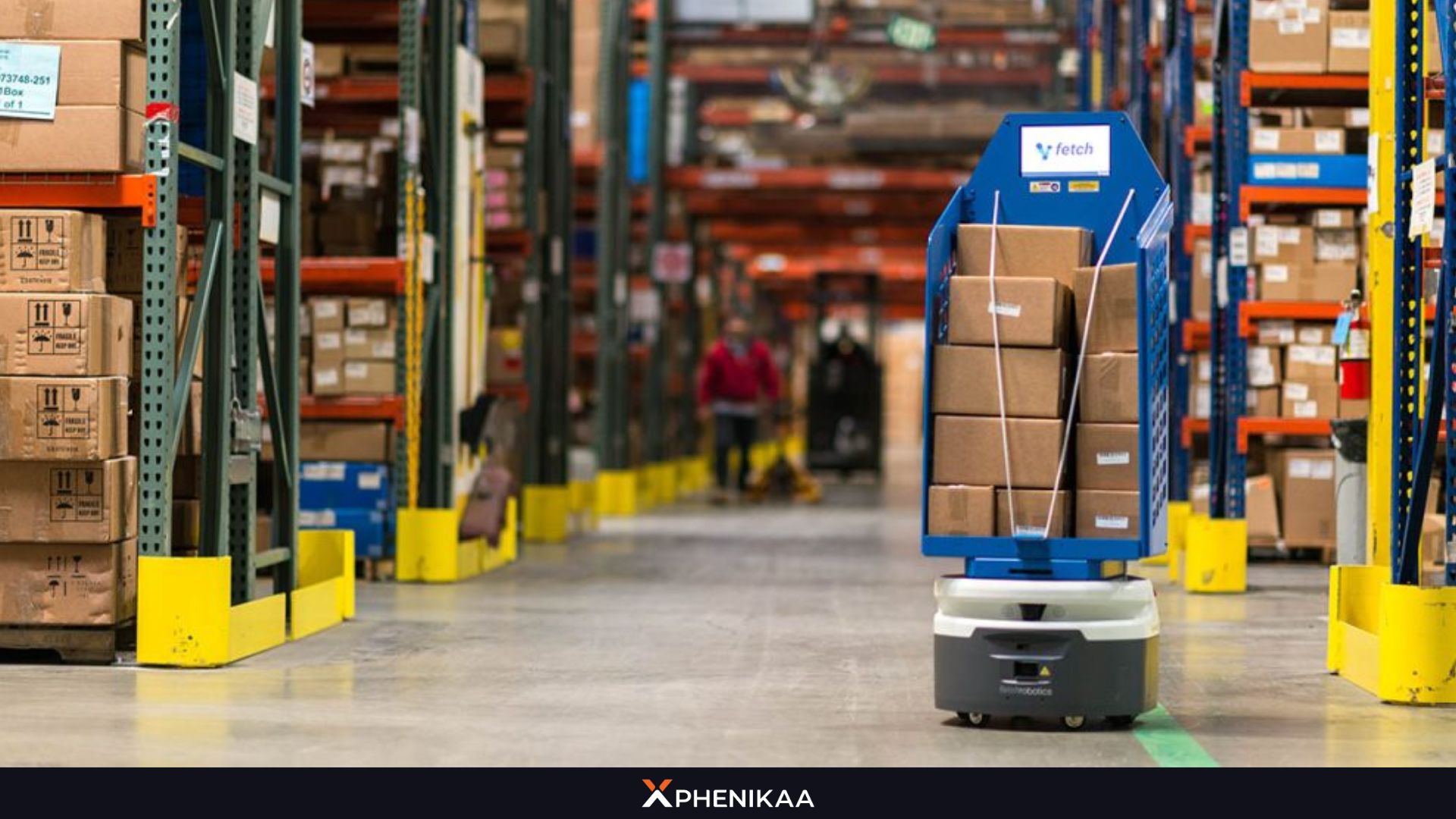

Automation Robots are now starting to gain recognition form big E-commerce companies like Alibaba, Amazon,… Their speed and efficiency are crucial for meeting the demands of same-day or next-day delivery, making AGV automation a vital asset in the E-commerce ecosystem.
2.5. Other Applications
Beyond these primary sectors, AGV robots are finding use in agriculture (transporting harvested crops), aerospace (moving large components), and even entertainment (automating set changes in theaters). Their ability to adapt to specific needs and environments underscores their status as a game-changer in automation, with new applications emerging as technology continues to evolve.
3. Types of AGVs
AGVs are not a one-size-fits-all solution. There are several distinct types of AGVs in use today, tailored to specific tasks and industries, ensuring that businesses can find the right robot for their unique requirements. Each of them have different design and AGV components installed. Here’s an overview of the most common types:
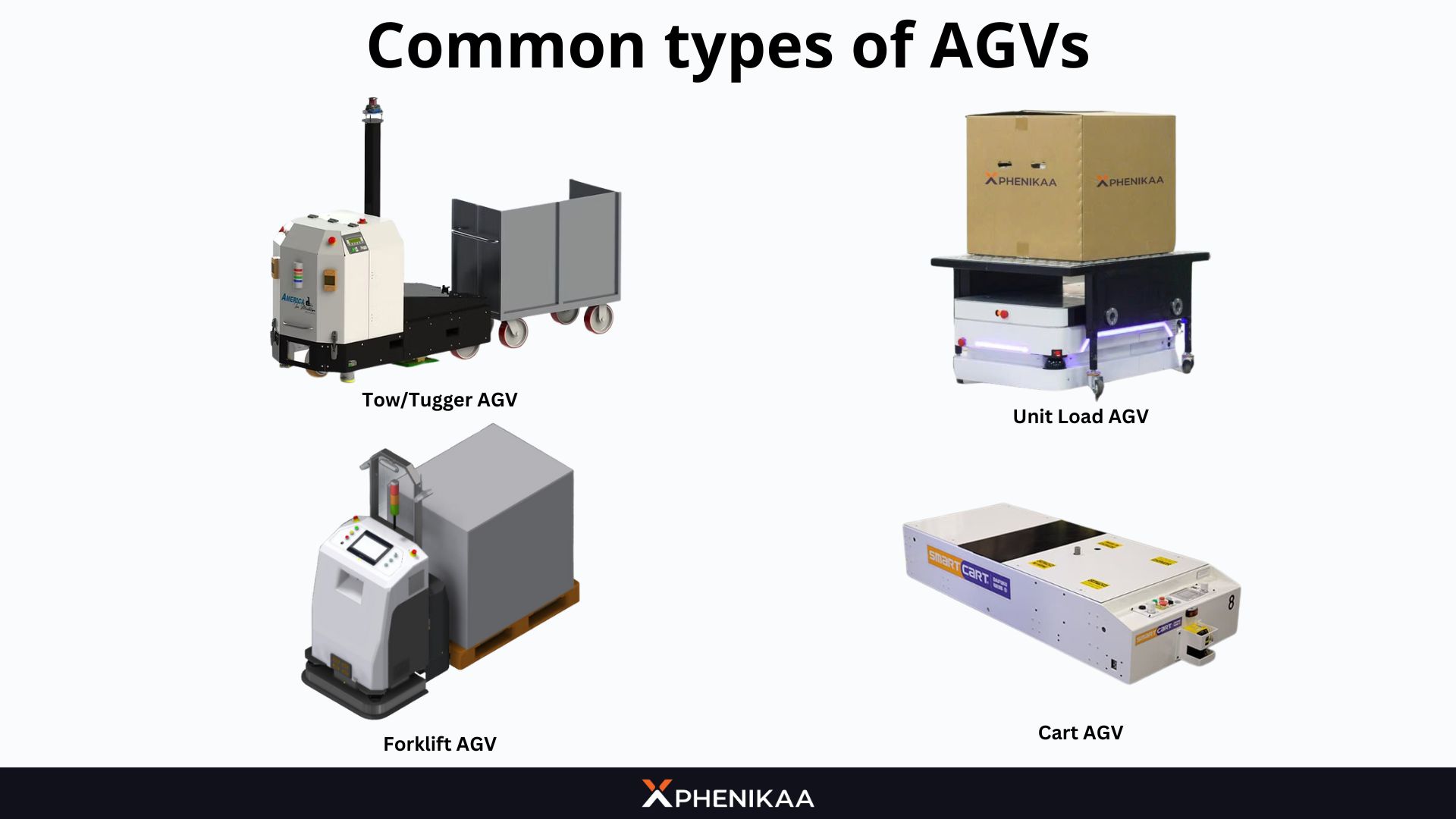
3.1. Tow/Tugger AGV
Tow or tugger AGV are designed to pull carts or trailers loaded with materials, making them ideal for heavy-duty transport in factories or large warehouses. These AGV can tow multiple loads at once, efficiently moving bulk materials across long distances. For example, in an automotive assembly plant, a tugger AGV might transport a train of carts filled with parts to various workstations, reducing the need for multiple trips.
3.2. Unit Load AGV
Unit load AGV are built to carry single, discrete loads such as pallets, containers, or racks. These vehicles excel in applications requiring precise deliveries, such as transferring a finished product from an assembly line to a storage area. Their design typically includes a flat deck or rollers to securely hold and unload the cargo, making them a popular choice in warehousing and manufacturing.
3.3. Forklift AGV
Forklift AGV mimics the functionality of traditional forklifts but operates autonomously. Equipped with forks or lifting mechanisms, they can pick up, transport, and stack goods at various heights. These AGVs are widely used in warehouses and distribution centers where vertical storage is common. For instance, a forklift AGV might lift a pallet of goods onto a high shelf, then retrieve another pallet from a lower level – all without human input.

3.4. Cart AGV
Cart AGV are smaller, more agile vehicles designed to navigate tight spaces and transport lighter loads. Often used in hospitals or small-scale warehouses, these AGVs can weave through narrow aisles or crowded areas with ease. A cart AGV might, for example, deliver tools to a technician in a factory or carry trays of supplies in a medical facility.
3.5. Hybrid AGV
Hybrid AGV combine features of multiple types, offering flexibility for varying tasks and environments. These vehicles might switch between towing, lifting, and carrying loads depending on the job at hand. Hybrid AGVs are particularly valuable in facilities with diverse workflows, as they can adapt to changing demands without requiring multiple specialized vehicles.
So, “which type of AGVs should I use?” you asked? Check the 07 AGV Vehicle Types: Which is the Most Common Of All? article written by Phenikaa-X’s engineers and find your answer, as well as learning about different AGV types and their applications.
4. The Benefits of AGVs
The growing adoption of AGV automation is no accident—businesses are drawn to the tangible benefits these vehicles provide. From cost savings to enhanced safety, AGVs offer a compelling case for investment. Let’s explore the key advantages in detail:
4.1. Increased Efficiency
AGV operates around the clock without the need for breaks or shift changes, significantly reducing downtime. Their ability to move materials quickly and consistently speeds up workflows, whether it’s transporting parts in a factory or shuttling packages in a warehouse. This tireless efficiency translates to higher productivity and shorter lead times.
4.2. Cost Savings
While the initial investment in AGV can be substantial, the long-term financial benefits are undeniable. By automating material handling, companies reduce labor costs associated with manual transport tasks.
Additionally, AGV minimizes human errors, such as misplaced items or damaged goods, that can lead to costly rework or replacements. Over time, these savings often outweigh the upfront expense.

4.3. Enhanced Safety
Safety is a critical concern in industrial environments, and AGVs are designed with this in mind. Equipped with sensors, cameras, and laser scanners, they detect obstacles, people, or other vehicles in their path, automatically adjusting their routes or stopping to avoid collisions. Features like emergency stop buttons and audible alarms further reduce the risk of accidents, making workplaces safer for human employees.

4.4. Scalability
As businesses grow or adapt to new demands, AGV offer remarkable scalability. Companies can add more vehicles to their fleet, reprogram existing ones for new tasks, or integrate them with updated systems—all without disrupting operations. This flexibility ensures that AGV remains a viable solution as industries evolve.
4.5. Consistency and Precision
Unlike human workers, who may be tired or make mistakes during repetitive tasks, AGV robots can perform with unwavering precision. They follow exact routes, handle loads with care, and deliver items to the correct locations every time. This consistency is especially valuable in industries like manufacturing, where precision is paramount.
4.6. Environmental Benefits
Modern AGV automations are powered by electric batteries, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering carbon emissions compared to traditional vehicles. In sustainability-focused industries, this eco-friendly aspect adds another layer of appeal to automation Robot adoption.
These benefits collectively position AGV as a smart investment for companies aiming to thrive in a technology-driven landscape. Whether it’s a small business seeking to optimize a single process or a global corporation overhauling its supply chain, AGVs deliver measurable value.
5. What Technology Makes AGV Special?
The magic behind AGV automated guided vehicles lies in their advanced technology. Let’s break it down:
5.1. Safety Systems
Safety is non-negotiable for Robotic and AGV Robots are no exception, especially in environments where they operate alongside humans or heavy machinery. These vehicles are equipped with an array of sensors such as ultrasonic, infrared and LiDAR – the most advanced sensor technology at the moment – to detect obstacles in real time. Cameras provide visual data, while laser scanners create detailed maps of the surroundings.

If an AGV senses a potential collision, it can slow down, reroute, or stop entirely. Additional safety features include emergency stop buttons, flashing lights, and audible alarms to alert nearby workers, ensuring a secure operational environment.
5.2. Navigation Systems
AGVs rely on sophisticated navigation technologies to move accurately and efficiently. The most common methods include:
- Magnetic Tape or Wires: Early AGVs followed fixed paths marked by magnetic tape or embedded wires in the floor. While simple and reliable, this method lacks flexibility for dynamic environments.
- Laser Guidance: Modern AGVs use laser triangulation, bouncing beams off reflectors placed around a facility to determine their position. This allows for precise navigation in complex layouts.
- Vision-Based Navigation: Cameras and image-processing software enable AGVs to “see” their surroundings, adapting to changes like moved obstacles or new pathways in real time.
- GPS or SLAM: For outdoor or highly dynamic settings, AGVs may use GPS or Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM), which builds and updates a map of the environment while tracking the vehicle’s location.
These navigation options allow AGV to suit a range of applications, from rigid factory floors to unpredictable warehouses.
5.3. Control Systems
AGV are managed by centralized software or onboard computers that coordinate their movements and tasks. In a large fleet, a control system might optimize routes to avoid traffic jams, prioritize urgent deliveries, or integrate with broader systems like WMS or enterprise resource planning (ERP) software. This intelligent orchestration ensures that AGV work harmoniously within the facility’s ecosystem.
Normally, manufacturers of the AGV often come with an AGV software compatible with their own AGV robot. But users can always connect the AGV with third party AGV software instead of the manufacturer’s default software. This allows for greater flexibility, as third-party AGV software may offer advanced features, better integration with existing systems. You can learn more about these AGV software in What is AGV Software? The Automated Guided Vehicle Control Systems.
5.4. Power Systems
Most AGV run on rechargeable batteries, providing hours of continuous operation. Advances in battery technology have led to faster charging times and longer lifespans, reducing downtime. Some models even feature battery-swapping stations, where an AGV replaces a depleted battery with a fully charged one in seconds, keeping operations running smoothly.
5.5. Cutting-Edge Innovations
The future of AGVs is being shaped by emerging technologies like:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI enables AGVs to learn from their environments, predict obstacles, and optimize routes over time.
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT connectivity allows AGVs to communicate with other machines, share data, and integrate into smart factories.
- Machine Learning: By analyzing past performance, AGVs can refine their operations, improving efficiency with each task.
Not to stop at that, engineers are working day and night to improve AGV systems, allowing them to collaborate with other smart systems and control applications, creating a Smart ecosystem for automation in all industrial facilities.
6. Common Questions About AGVs
As AGVs gain popularity, they spark curiosity and questions. Here are answers to some of the most frequently asked questions Phenikaa X received:
-
What does AGV mean?
As mentioned at the beginning of this article, AGV stands for Automated Guided Vehicle – a robotic system designed to transport materials autonomously without human drivers.
-
How do AGV differ from AMR?
AGV follows fixed or guided paths (magnetic tape or laser reflectors), while AMR uses AI and advanced sensors to navigate freely and adapt to obstacles without predefined routes.
You can check the comparison between these two type of robots in AGV vs AMR – Key Differences Comparison and Which Should You Choose. Our Engineer marks down all differences to help you understand these technologies better.
-
Are AGVs expensive?
Surely, AGV is considered to be a big investment for most companies. The upfront cost of AGV robot can be high, depending on their complexity and features. Normally it is anywhere between $15.000 – $200.000.
However, their efficiency, reduced labor costs and long-term reliability often result in a strong return on investment (ROI).
-
Can AGVs work with humans?
Yes! Advanced safety systems and collaborative designs allow AGVs to operate safely alongside human workers, enhancing rather than replacing human efforts.
-
How are AGVs programmed?
AGVs are typically programmed via software that defines their routes, tasks, and interactions. Some use simple path-following algorithms, while others leverage AI for adaptive behavior.
Conclusion
Automated Guided Vehicles are more than just robotic transporters—they’re a symbol of the automation revolution sweeping through modern industries. The benefits of AGVs – increased efficiency, cost savings, enhanced safety, scalability, and precision – make them a smart investment for businesses looking to stay ahead in a competitive, tech-driven world.
Curious about adopting this technology? Join Phenikaa X today and explore AGV solutions or consult an expert to see how AGVs in manufacturing can transform your operations.
Contact us:
- Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/phenikaa.x
- Hotline: (+84) 904530545
- Email: contact@phenikaa-x.com

