Robotics and Automation are currently hot topics of interest for businesses in the manufacturing and warehousing sectors, yet they are frequently confused. So, what exactly is Robotics? What is Automation? What are the key differences between Robotics and Automation? Let’s explore the details together with Phenikaa-X in this article.
1. What Are The Fundamental Concepts Of Robotics And Automation?
Robotics refers to the engineering discipline involving the design, construction, operation, and application of intelligent machines (robots). Automation is the technology by which a process or procedure is performed without human assistance. Both aim to enhance efficiency and productivity.
Robotics and automation represent two interconnected yet distinct pillars of modern industrial transformation. Understanding their definitions is the first step toward strategic implementation.
1.1. What is Automation?
Automation refers to machinery systems created by humans to assist in performing tasks with minimal intervention. It encompasses a wide spectrum of systems – mechanical, electrical, software-based, or hybrid – that execute predefined processes automatically. These automation systems can operate entirely on their own by repeatedly executing pre-programmed operations, or carry out tasks under the control of specialists.

At its essence, automation is about process independence. It transforms manual, repetitive, or rule-based operations into self-regulating workflows. This can range from a simple timer-controlled irrigation system to an AI-driven warehouse management platform coordinating thousands of transactions per minute.
Key characteristics of automation:
- Focuses on system-level efficiency
- Reduces dependency on human decision-making in routine operations
- Integrates hardware, software, sensors, and control logic
- Applicable across industries: manufacturing, logistics, energy, healthcare, and more
1.2. What is Robotics?
Robotics, on the other hand, is the science and engineering of designing, building, operating and applying physical robots – programmable machines capable of carrying out complex actions autonomously or semi-autonomously. They are distinguished by their ability to perceive, process information and act. While all robots are part of automation, not all automation involves robots.

A robot is a tangible, movable machine equipped with:
- Sensors (vision, touch, proximity)
- Actuators (motors, grippers, arms)
- Controllers (onboard computers or external PLCs)
- AI/ML algorithms (for adaptive behavior)
Unlike general automation, robotics emphasizes physical interaction with the environment. Robots mimic or surpass human capabilities in dexterity, strength, speed, or endurance.
Example: A 6-axis articulated robot welding a car frame with sub-millimeter precision, adjusting in real-time to material variations.
2. Key Different Between Robotics And Automation
While robotics and automation are often conflated, their differences are critical for informed investment and system design.
|
Criteria |
Automation |
Robotics |
| Core Focus | Process autonomy – making entire workflows self-sustaining | Physical agency – enabling machines to act in the real world |
| Technology Stack | PLCs, SCADA, ERP, WMS, IoT, sensors, conveyors | Manipulators, end-effectors, vision systems, AI navigation, motion control |
| Flexibility | High in logic reconfiguration (software updates) | High in physical adaptability (reprogrammable paths, tool changes) |
| Implementation Scale | System-wide (factory floor, supply chain) | Task-specific (welding station, picking zone) |
| Human Interaction | Minimal during operation | Collaborative (cobots) or isolated (industrial robots) |
| Example | Automated inventory tracking via RFID + WMS | Robotic arm depalletizing mixed-SKU boxes |
From the chart above, we can summary some key different between Robotics and Automations:
- Automation focuses on comprehensive process autonomy, using PLCs, SCADA, ERP, WMS, IoT, and conveyors to optimize large-scale systems with minimal human intervention.
- Robotics emphasizes physical agency, relying on manipulators, end-effectors, vision systems, and AI navigation to execute specific tasks.
- Flexibility: Automation excels in logic reconfiguration via software; Robotics stands out in adjustable paths and physical tool changes. Most of the time, Automation systems are fixed while robotics can be mobile.
- Scale: Automation applies across entire factories/supply chains; Robotics is limited to stations like welding or picking zones.
- Human interaction: Automation requires almost none; Robotics enables collaboration (cobots) or isolation.
3. Automation and Robotics Application Comparison
The synergy and distinction between robotics and automation become most visible in manufacturing and warehousing – two sectors where precision, speed, and reliability define success.
3.1. Manufacturing Applications
For manufacturing operations in workshops and factories, automation is the longest-standing and most widely adopted solution of all, utilized by the vast majority of businesses worldwide. Production activities in these environments are typically standardized and repetitive, which is why companies tend to opt for simple, easy-to-deploy automation models to support or replace human labor across various stages.
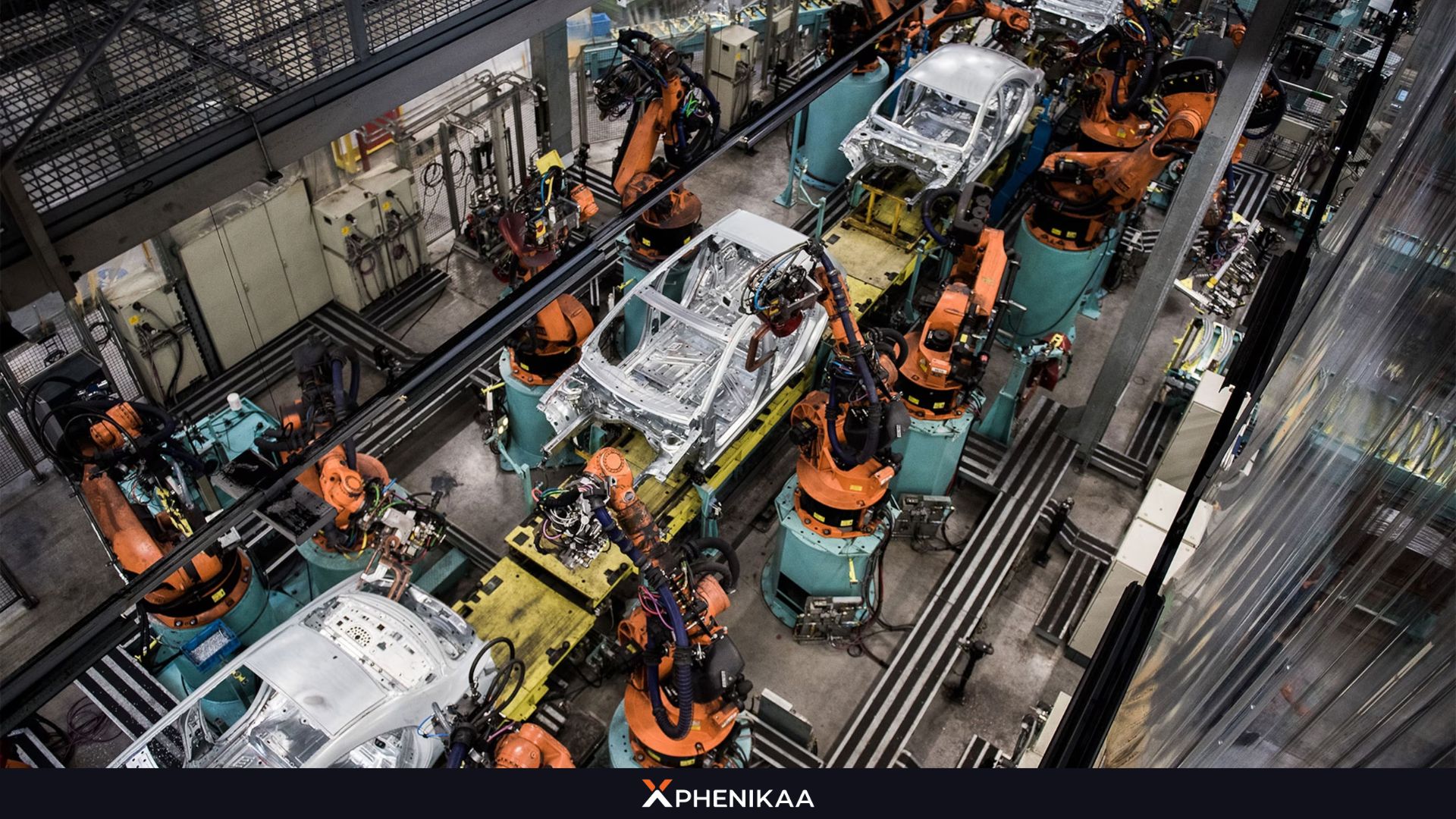

A clear and basic example is readily apparent: It is not difficult to encounter high-tech factories employing robotic arms or automated conveyor systems and assembly lines. This is especially true for factories specializing in high-precision electronic component manufacturing, automotive assembly plants and other similar facilities.
|
Function |
Automation |
Robotics |
| Process Control | PLCs sequence machines; SCADA monitors KPIs | Robotic arms execute welding, painting, assembly |
| Material Flow | Conveyor systems, automated guided carts | AGVs, AMRs transport parts between stations |
| Quality Assurance | Vision systems auto-reject defects | Cobots perform tactile inspections alongside humans |
| Data Integration | ERP syncs production with supply chain | Robots feed real-time cycle time data into MES |
3.2. Warehousing & Logistics Applications
In the warehousing and logistics sector, the majority of tasks still require human hands, supported by simple automation devices such as forklifts and overhead cranes. However, in recent years, AMR (Autonomous Mobile Robots) and AGV (Automated Guided Vehicles) have been increasingly valued by enterprises due to their ability to significantly enhance labor productivity.

Autonomous robot models like AMR and APM (AMR equipped with forklift systems) are gradually replacing traditional pallet trucks and conventional forklifts. These robots operate fully automatically and can be easily managed – hundreds at a time – using just a single computer and monitoring screen. This technology is attracting attention from industry giants and is being practically implemented by leading names such as Alibaba, Samsung, Amazon…
|
Function |
Automation |
Robotics |
| Inventory Management | WMS tracks stock; AS/RS stores/retrieves pallets | AMRs move goods-to-person |
| Order Fulfillment | Conveyor sorters route packages | Robotic arms pick, pack, label |
| Space Optimization | Vertical storage carousels | Dense mobile racking navigated by AMRs |
| Last-Mile Prep | Automated dimensioning/weighing | Delta robots sort parcels by destination |
However, this does not mean we can definitively claim that automation surpasses robotics, or vice versa. Both systems are fundamentally designed to enhance labor productivity, eliminate human error and reduce operational costs for businesses. In reality, large-scale factories and warehouses strategically deploy both technologies in parallel to achieve the greatest competitive advantage.
4. What Are The Benefits Of Robotics And Automation For Manufacturing?
The adoption of robotics and manufacturing automation offers a transformative impact on production environments. Companies leveraging these technologies often experience a significant competitive edge.
4.1. Automation Enhance Productivity And Efficiency
Automation significantly boosts productivity by enabling continuous operation, reducing cycle times, and minimizing human intervention in repetitive tasks. This leads to higher output volumes and a more efficient use of resources, directly contributing to improved overall operational efficiency.
One of the most immediate benefits of industrial automation robotics is the drastic improvement in productivity. Robots can operate continuously, 24/7, without fatigue or breaks, performing tasks at a consistent speed and quality. This leads to substantially higher throughput compared to manual labor.
For example, a robotic welding cell can complete welds 2-4 times faster than a human welder, with greater precision and consistency.
Furthermore, automation streamlines processes by reducing bottlenecks and optimizing material flow. This creates a more agile and responsive production system, minimizing lead times and allowing companies to meet demand more effectively.
4.2. Robotics And Automation Impact On Product Quality And Consistency
Human error is an inevitable part of manual production. Robots, however, perform tasks with exceptional precision and repeatability, virtually eliminating variation. This translates to a significant improvement in product quality and consistency. For instance, in electronics manufacturing, robotic assembly can achieve tolerances far beyond human capability, leading to more reliable and higher-performing devices.
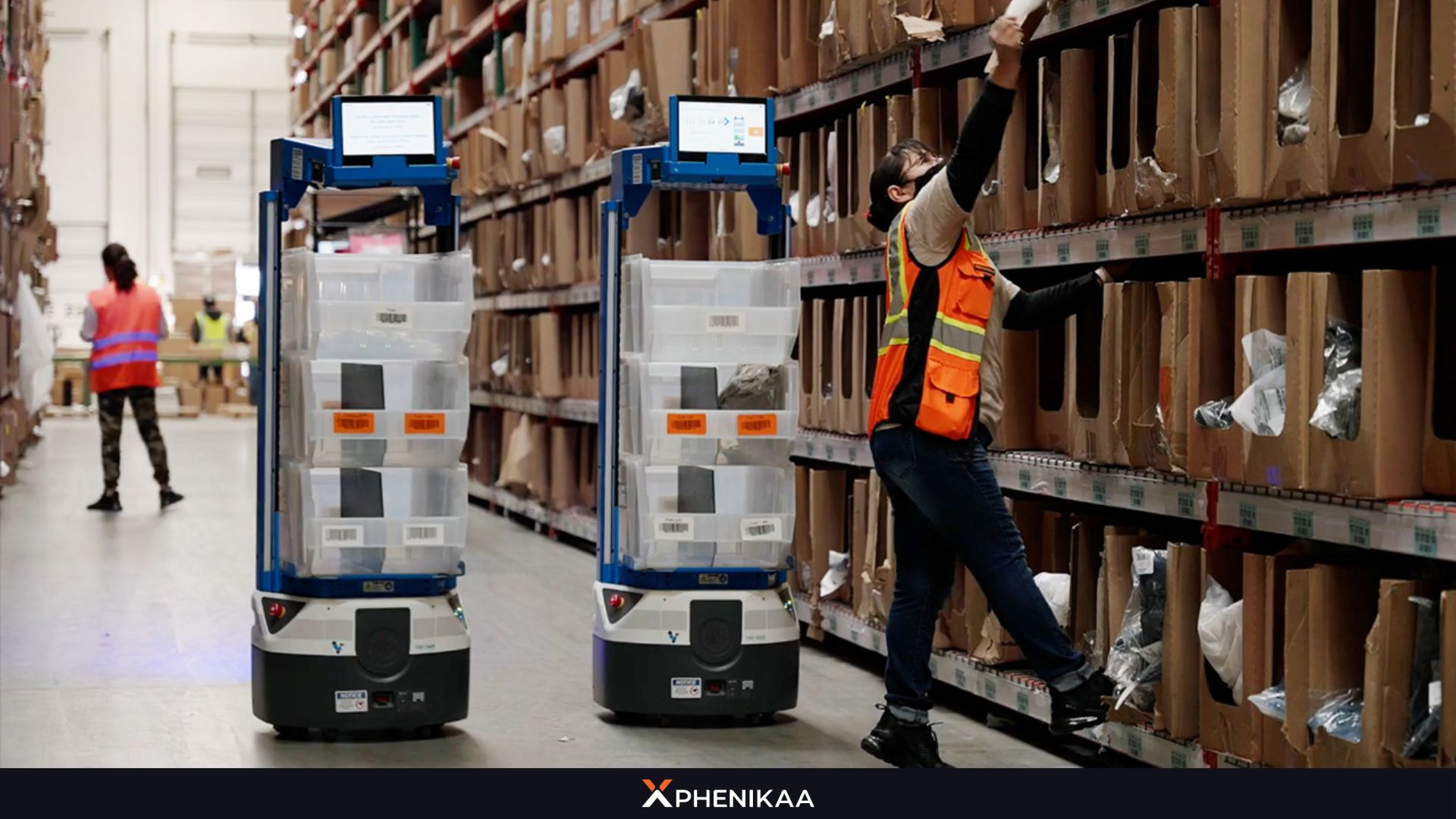

- Elimination of Human Error: Unlike manual workers prone to fatigue, distraction or inconsistency, robots follow programmed paths repeatedly, preventing mistakes like misaligned components or incorrect torque application.
- Consistent Process Parameters: Robots maintain consistency and speed, unaffected from pressure, temperature, and timing across millions of cycles of the same task.
- Reduced Defect Rates: Fewer errors in the production process mean fewer defective products, thereby reducing wasteful consumption of raw materials.
- Traceability and Quality Data: Every robotic action is logged with timestamps and sensor data, enabling root-cause analysis of rare defects and continuous process improvement.
- Lower Rework and Scrap Costs: Fewer defects translate to 50–80% reduction in material waste and labor hours spent on corrections, directly boosting profitability.
4.3. How Does Robotics And Automation Contribute To Cost Reduction And Improved ROI?
While the initial investment in industrial automation robotics can be substantial, the long-term cost savings and improved Return on Investment (ROI) are compelling.
- Reduced Labor Costs: Automating repetitive or hazardous tasks allows companies to reallocate human workers to more complex, value-added roles, optimizing workforce utilization.
- Minimized Waste: Precision and consistency lead to less scrap material, reducing waste and associated costs.
- Lower Energy Consumption: Modern robots and automated systems are often designed for energy efficiency, contributing to reduced utility bills. For example, a study published in the “Journal of Manufacturing Systems” found that robotic cells could reduce energy consumption by up to 15-20% compared to traditional manual operations in certain applications.
- Increased Throughput: Higher production volumes with fewer errors mean more products reaching the market faster, generating more revenue.
| Benefit Category | Description | Quantitative Impact (Example) |
| Productivity Boost | 24/7 operation, reduced cycle times, optimized resource utilization. | Up to 400% faster cycle times in specific tasks. |
| Enhanced Quality | Elimination of human error, high precision and repeatability. | Reduction of defects by over 50%. |
| Cost Reduction | Lower labor costs, minimized waste, optimized energy use. | Average payback period of 1-2 years for robot investments. |
| Improved Safety | Removal of humans from hazardous or repetitive tasks. | Up to 70% reduction in certain industrial accidents. |
| Flexibility & Scalability | Adaptation to product changes and production volume fluctuations. | Rapid retooling for new product lines, reducing downtime by 20-30%. |
These compelling benefits underscore why businesses are increasingly turning to industrial robotics automation to stay competitive in a rapidly evolving global market.
5. Future Applications of Robotics And Automation
The future of robotics and automation is defined by increased collaboration between humans and machines, enhanced intelligence through AI and machine learning, and broader adoption across non-traditional sectors. These trends promise to unlock unprecedented levels of efficiency, innovation, and societal impact.
The landscape of automatics and robotics is continuously evolving, driven by technological advancements and increasing demand for intelligent solutions. Staying abreast of these trends is vital for businesses to maintain a competitive edge. Phenikaa-X actively integrates these emerging technologies into its automation & robotics solutions.
5.1. Robotics and Automations Are Slowly Changing The Workplace
Robots and Automations nowadays are revolutionizing with AI and all advanced technology, allowing them to work safely alongside humans without the need for extensive safety caging. This allows for optimal utilization of both human dexterity and cognitive abilities, and robotic strength and precision.
These machinery and systems are increasingly used for tasks such as:
- Assembly: Assisting workers with repetitive or ergonomically challenging assembly tasks.
- Machine Tending: Loading and unloading machines, allowing human operators to focus on supervision and quality control.
- Inspection: Performing automated visual inspections while humans handle complex decision-making.
- Packaging: Assisting with delicate or varied packaging tasks.
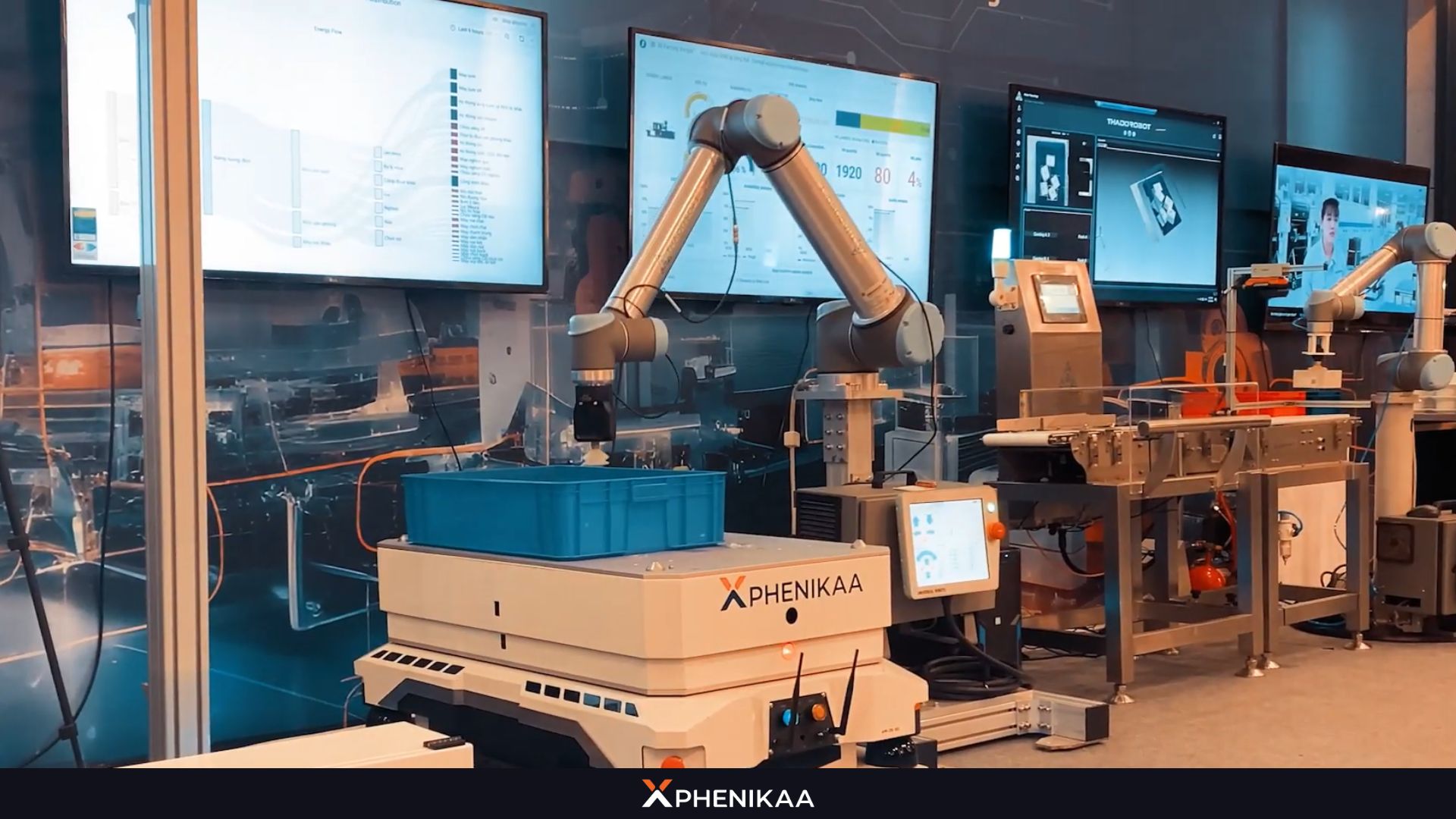

This blend of capabilities underscores the growing importance of automation with robotics in fostering more dynamic and adaptable manufacturing environments.
5.2. The Role of AI In Advancing Robotics And Automation
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning is propelling robotics and automation into new frontiers. AI empowers robots to not just perform tasks but to learn from their environment, adapt to changing conditions, and make intelligent decisions. This shift is critical for handling unstructured or unpredictable environments where pre-programmed actions are insufficient.
At Phenikaa-X, we have gradually developed proprietary AI algorithms tailored for the robot models we manufacture. The AI is fed with data customized to the specific working environment, product type, and requirements provided by our partners. This ensures that Phenikaa-X products deliver optimal performance for each individual customer.
5.3. Some Applications Of Robotics In Non-Traditional Sectors
While industrial automation robotics has traditionally focused on manufacturing, the applications of robotics and automation are rapidly expanding into diverse, non-traditional sectors.
- Healthcare: Surgical robots assist in minimally invasive procedures, improving precision and reducing patient recovery times. Phenikaa Mec – The hospital system of Phenikaa, has already adopted Service Bot to the action.
- Agriculture: “Agribots” perform tasks like automated planting, harvesting, and crop monitoring, increasing yield and reducing labor costs. For example, robotic harvesters can pick fruits with greater speed and less damage than human workers.
- Logistics and Warehousing: Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMR) and Automated Guided Vehicles (AGV) transport goods within warehouses, optimizing inventory management and order fulfillment.
- Service Industry: Robots are being deployed in hospitality for tasks like room service delivery, and in retail for inventory management and customer assistance.
- Construction: Robots can perform dangerous tasks like demolition, bricklaying, and even 3D printing of structures, improving safety and efficiency on construction sites.

These expanded applications demonstrate the versatility and transformative power of modern robotics, offering solutions that were once considered futuristic..
Discover how Phenikaa-X can elevate your business with innovative and reliable robotics and automation solutions. We are eager to help you unlock the full potential of advanced automation.
- Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/phenikaa.x
- Hotline: (+84) 904530545
- Email: contact@phenikaa-x.com