In today’s fast-paced world, industries are increasingly turning to automation to streamline operations, reduce costs, and stay competitive. One of the most promising innovations in this space is Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMR). So what is an AMR robot? Let’s dig in together with Phenikaa-X right now and find out all about this fresh new industrial technology.
1. The Introduction to Autonomous Mobile Robots – AMR Robots
What is AMR robot?
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMR) or AMR robots are advanced robotic systems designed to move and operate independently in dynamic environments without the need for human intervention or predefined paths. Unlike traditional robots, AMR is equipped with sophisticated sensors, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning capabilities, enabling them to navigate complex spaces, avoid obstacles, and perform tasks efficiently.
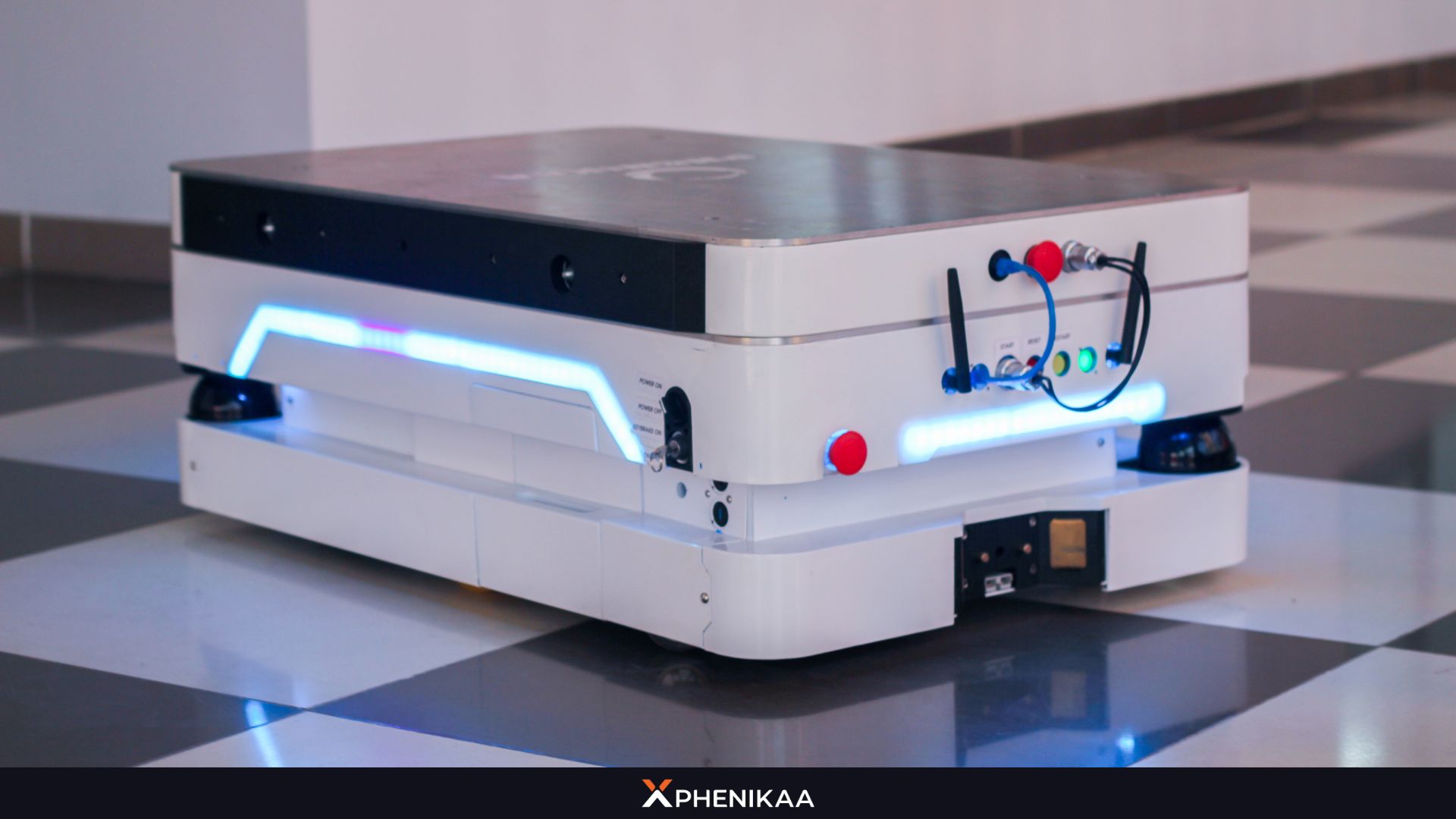

The vision behind the AMR robot is simple yet powerful: create intelligent machines that handle repetitive, labor-intensive jobs autonomously. By blending robotics with cutting-edge sensing and computing tech, these robots excel in unpredictable settings, adapting to diverse tasks and evolving conditions. Imagine an AMR robot that learns from its surroundings, optimizes its performance in real time, and doesn’t rely on pre-set routes—that’s the dawn of adaptable, smart automation.
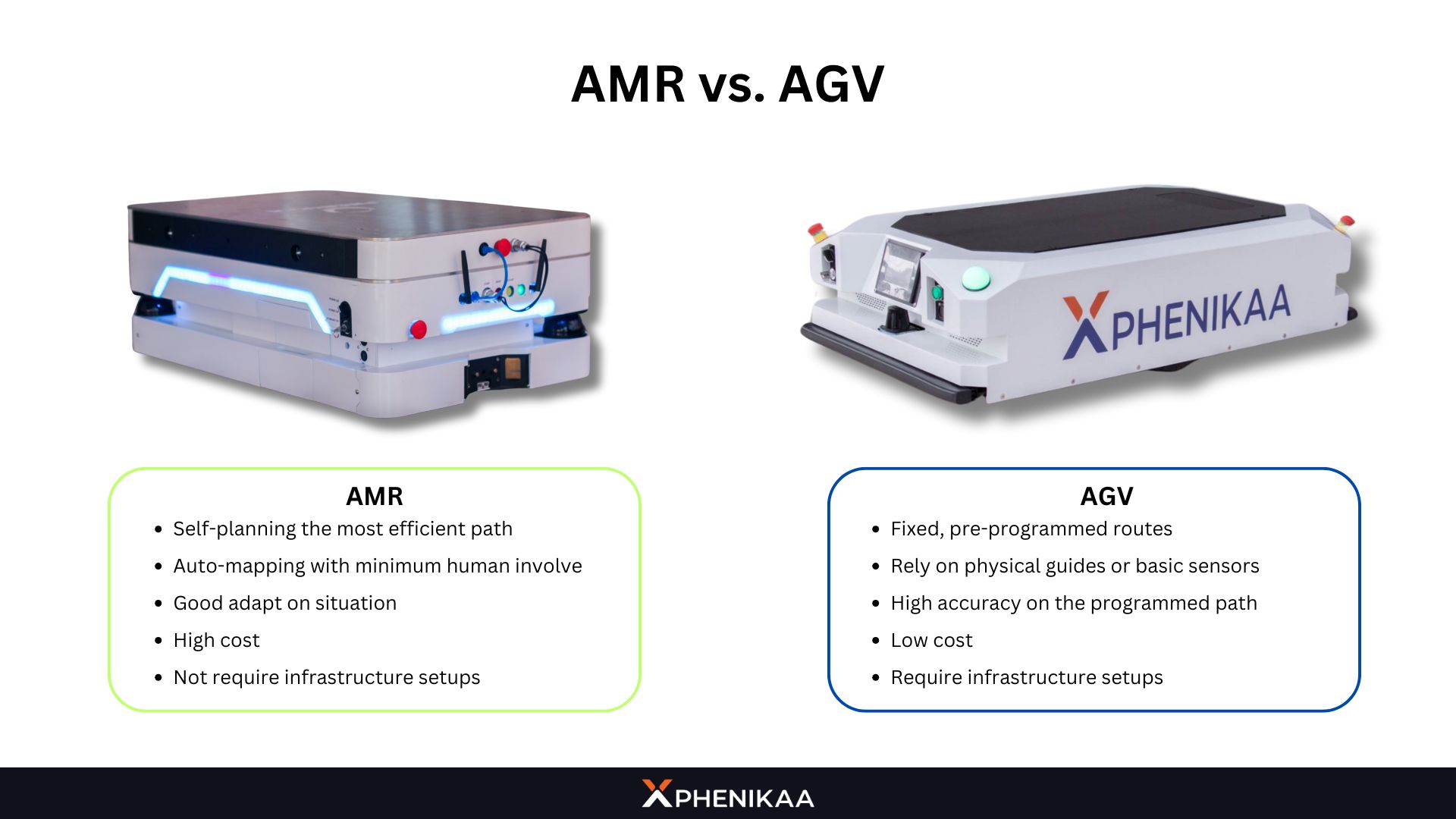
AMR vs. AGV: What’s the Difference?
While AMR and Autonomous Guided Vehicles (AGV) are both used for automation, they differ significantly in functionality. The key difference is about the way their navigation system works, or in short, is the way they move around the facility.
AGV’s navigation system is very simple: You give it fixed routes and it will follow. The routes often require physical guides like wires or magnetic strips, and lack the flexibility to adapt to changes in their environment.
In contrast, AMR robots use advanced navigation technologies to move freely, making them more adaptable and versatile for dynamic settings. With such, the Robot can be equipped with more advanced detection technologies for human safety, such as obstacle avoidance, human detection,…
For further detail about what makes AMR different from AGV, check this article AGV vs AMR made by Phenikaa-X’s engineers.
Growing Popularity of AMR
AMRs are gaining traction across industries due to their ability to streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve human safety. From warehouses, healthcare facilities to agriculture and retail, businesses are increasingly adopting AMRs to enhance productivity and stay competitive in a rapidly evolving technological landscape.
Here is some collective reports we found while researching about AMR:
- According to a report by Allied Market Research, the global Autonomous Mobile Robot market is projected to reach $14.5 billion by 2026, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 21.5% from 2019 to 2026
- A 2019 survey by McKinsey & Company found that 50% of warehouse operators planned to increase their investment in robotics, including AMRs, over the next few years.
- Since acquiring Kiva Technologies in 2012, Amazon has integrated robots into their fulfillment centers to improve efficiency and reduce human labor costs.
2. How does AMR Work?
AMR robots operate by utilizing a combination of advanced technologies that enable them to navigate, perform tasks, and adapt to dynamic environments independently.:
2.1. Navigation and Mapping
AMR uses a technology known as Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) to navigate. SLAM allows the robot to create real-time maps of its surroundings while simultaneously tracking its position within those maps.
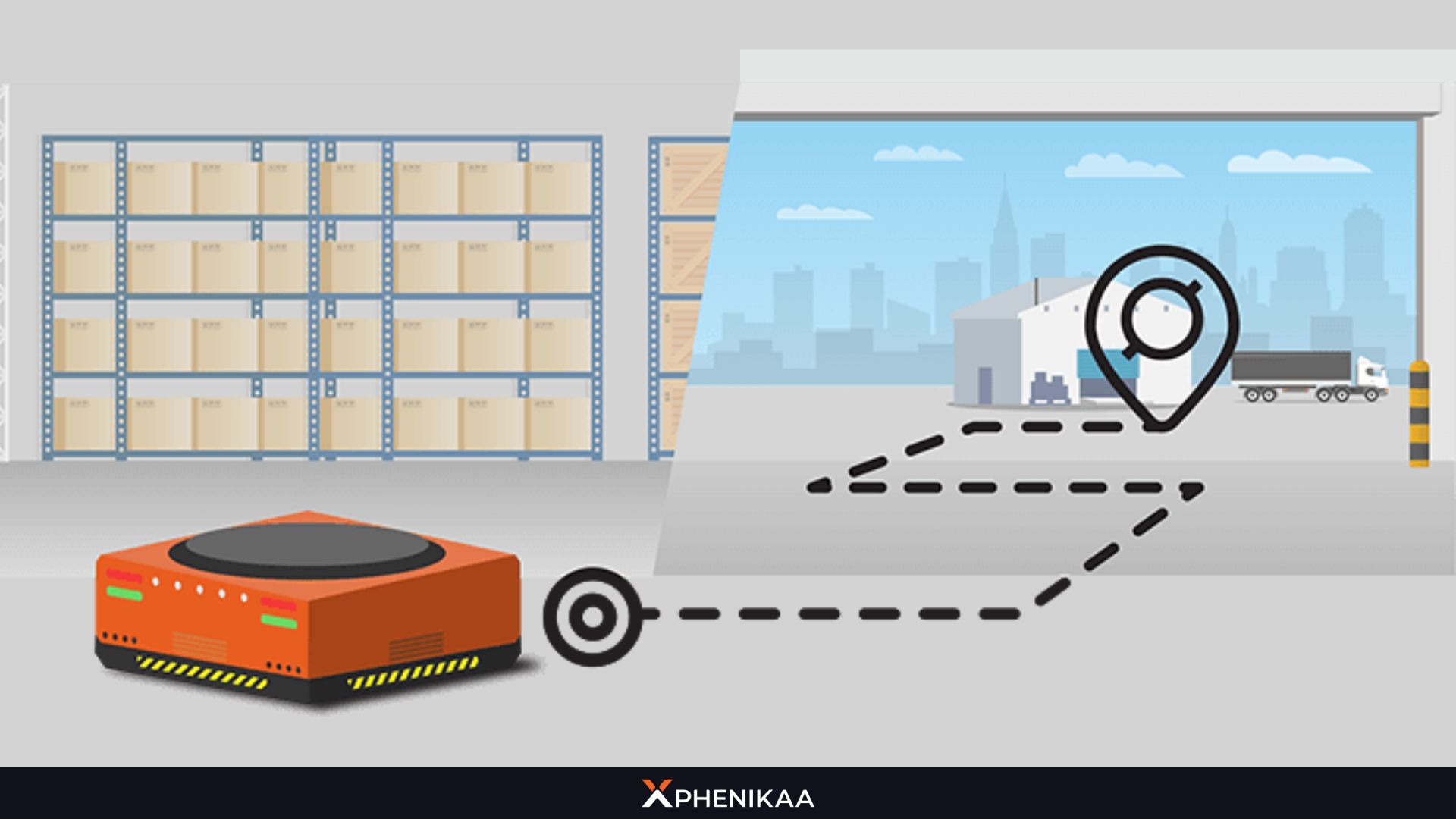

This capability is essential for AMR Robot to move autonomously without relying on predefined paths or guides. The robot can continuously update its map as it encounters new obstacles or changes in the environment.
2.2. Sensors and Perception
AMR are also equipped with various sensors, including LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), cameras, ultrasonic sensors, and infrared sensors, which allow them to “see” and interpret their environment. These sensors help the robot detect obstacles, measure distances, and identify objects. With the data collected from these sensors, AMRs can avoid collisions, find the most efficient path, and ensure smooth operation in dynamic spaces.
2.3. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
AMR robots leverage AI and machine learning algorithms to make decisions and improve their performance over time. AI enables AMRs to process the data from their sensors, analyze different scenarios, and make informed decisions based on the environment and the tasks at hand.
As the AMR robot encounters new obstacles or challenges, it can learn from the experience and improve its future responses. This method is also known as AI training.
2.4. Task Execution and Adaptability
Once the AMR has mapped its environment and understands its surroundings, it can perform a range of tasks such as transporting materials, inventory management, or even disinfection in healthcare settings. The flexibility of AMRs is one of their most significant advantages, as they can be reprogrammed or adapted to perform different roles across various industries.
2.5. Communication and Integration
One of the key features that make AMRs highly versatile and user-friendly is their ability to communicate and integrate with existing systems through intuitive controlling software. The software is designed to be compatible with computers, tablets, or smartphones and acts as the bridge between human operators and the autonomous robots, enabling users to monitor, control, and interact with AMRs in real-time.
As AMR technology continues to advance, user interfaces and control systems will likely become even more sophisticated, offering more seamless interaction and greater control, making AMRs an increasingly essential tool for businesses seeking automation solutions.
Interest in how AMR work and what technologies make them special? You can read all the detail about AMR in this article How Do Autonomous Mobile Robots Work – AMR Anatomy Breakdown, shared by Phenikaa-X’s Engineers.
3. Key Features of AMR
So what makes AMRs so special? It’s not very hard to realize how useful they can be in any industrial environment. Some of their key features are:
Autonomous Movement
AMRs do not require predefined paths or human intervention. At installation, users can “tour” the AMR’s system so that it will map the workspace themselves via sensor to detect walls, machinery, interior and define the roadmap. With that, they can navigate complex environments independently, making them ideal for dynamic settings like warehouses and hospitals.
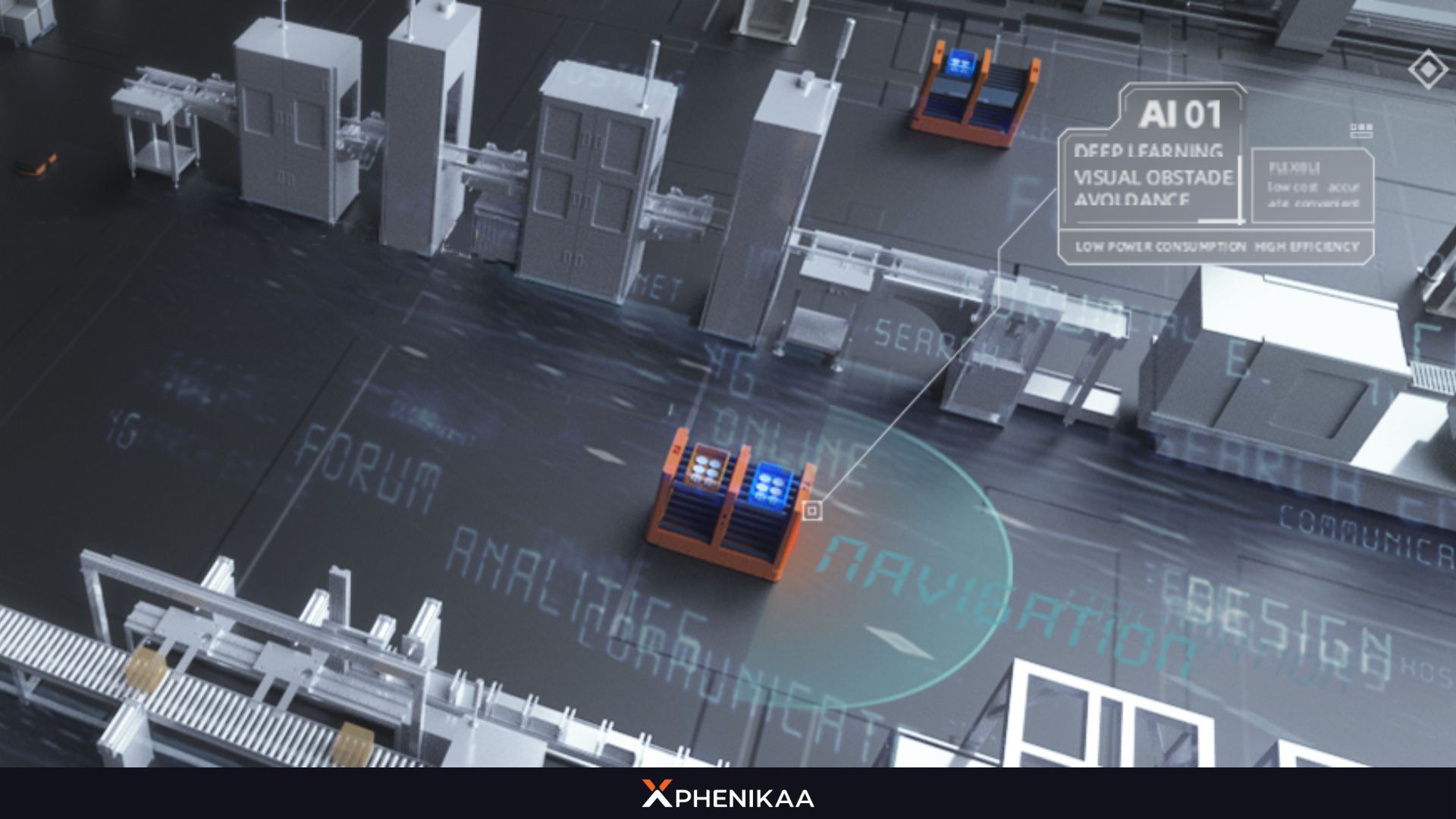

Collision Avoidance and Navigation
Equipped with advanced sensors and AI, AMRs can detect and avoid obstacles in real-time. They can reroute themselves to ensure smooth operations, even in crowded or changing environments.
What makes AMR even more powerful is their AI-driven learning capability. As they encounter new environments and navigate through them, they “learn” from their experiences. This means that AMR can adapt to new paths and roadways by updating their internal maps, improving their navigation strategies over time.
Flexibility
AMRs are highly adaptable, capable of performing a wide range of tasks. They also can be easily modified into different variants to suit specific operational needs by the manufacturer. For example, the same AMR platform can be equipped with various attachments or specialized modules, such as conveyor belts for transporting goods, UV lights for sanitation, or cameras for surveillance and inspections.
This adaptability allows AMR to seamlessly transition between different tasks, making them a highly cost-effective solution for businesses that require both flexibility and efficiency.
4. Types of Autonomous Mobile Robots
Depending on the needs of each industry, AMRs can be modified to meet the working requirements. As such, there are 05 main types of AMRs being used at the moment:

4.1. Platform AMR
A Platform AMR is a basic type of AMR designed with a flat, versatile surface called “platform”, intended to carry and transport various payloads in a facility. They are widely used in industries like logistics, manufacturing, and warehousing. The “platform” design distinguishes them by their ability to support a range of items, from boxes and bins to custom containers, making them highly adaptable to diverse operational needs.
4.2. Manual loading AMR
Manual loading AMR is the standard AMR robots designed to transport goods or materials that are loaded onto it manually by human operators, rather than through an automated loading system. Without robotic arms or conveyor integration, a manual loading AMR relies on a person to place the payload (e.g., boxes, trays, or materials) onto its platform or designated carrying area.
4.3. Autonomous AMR Forklifts
Autonomous AMR Forklifts are a type of AMR Robot designed to lift, transport, and stack palletized loads without human intervention. They combine the traditional functionality of a forklift – used for moving heavy goods in warehouses, factories, and distribution centers—with advanced robotic autonomy.
Learn detail about AMR forklift in this article: What Are AMR Forklifts? Top Benefits for Industries.
4.4. Sortation AMR
Sortation AMR are robots engineered to automate the process of sorting items into specific categories, destinations, or orders within a facility. These AMR are commonly deployed in warehouses, factories and distribution centers to streamline the handling of goods after picking or during processing, ensuring they reach the correct bins, chutes or shipping areas efficiently
4.5. Picking AMR
Picking AMR is a specialized type of AMR designed to assist with or fully automate the process of picking items – selecting and retrieving specific goods – from shelves or storage areas. The robot came up with advanced robotic arms and vision systems, allowing it to correctly identify and separate products.
There are still many more types of AMR Robot, such as Conveyor AMR, Cobots with Manipulator, Heavy AMR, Pallet Jack AMR,… built to be suitable for different needs of use. You can learn more about AMR types in this article, with split into 04 different categories by usage.
5. Benefits of AMR
5.1. Increased Efficiency and Productivity
Autonomous Mobile Robots transform workplace efficiency by automating repetitive, time-consuming tasks such as material transport and inventory handling. This automation allows human workers to shift their focus to higher-value activities – like problem-solving, innovation, or quality assurance – significantly boosting overall productivity. For instance, in a warehouse, AMRs can handle routine stock movement, enabling staff to prioritize order customization or process optimization, driving faster and more effective operations.
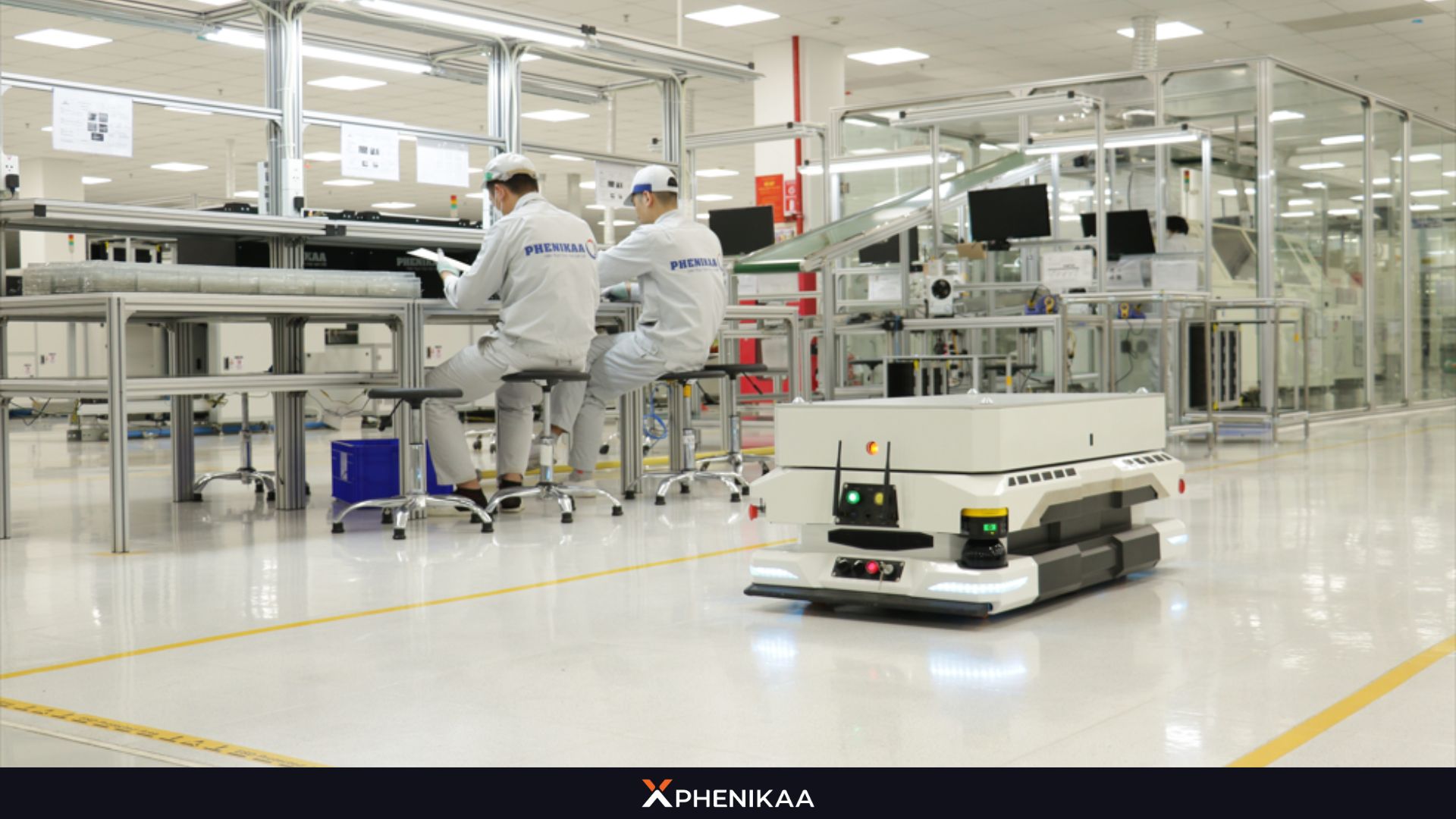

5.2. Enhanced Worker Safety
AMR excel in environments where human safety is at risk, such as chemical plants, construction sites, or areas with heavy machinery. By taking on hazardous tasks – handling toxic substances, navigating unstable terrain, or operating in confined spaces – these robots minimize workers’ exposure to danger, reducing the likelihood of injuries. Their advanced sensors and collision-avoidance systems further ensure safe coexistence with human teams, making them a vital tool for improving workplace safety standards.
5.3. Cost Savings
Although the upfront cost of deploying AMR can be substantial, their long-term financial benefits are compelling. By reducing reliance on manual labor for repetitive tasks, AMR lower payroll expenses and mitigate costs associated with human error, such as damaged goods or delays. Additionally, their ability to optimize workflows – through efficient navigation and task execution – enhances operational efficiency, delivering a strong return on investment over time, especially in high-volume or continuous-operation settings.
5.4. Improved Flexibility and Scalability
AMRs offer unmatched versatility, seamlessly integrating into existing systems without requiring extensive infrastructure changes. Their adaptability allows businesses to reprogram or reconfigure them for new tasks, while their modular designs support customization to meet specific needs. Scalability is a key advantage – companies can start with a small fleet and expand as demand grows, making AMRs a practical solution across industries, from small warehouses to sprawling manufacturing plants.
Depend on the field AMR implemented in, there are quite alot of different benefits AMR can bring to your business. Check this article to learn about 10 AMR Advantage in different fields of industry.
6. Real-World Applications of AMR Robot
As technology continues to evolve, Autonomous Mobile Robots are slowly but steadily making their way into real-world applications across various industries. While once considered a futuristic concept, AMRs are now becoming an integral part of operations and found their own recognitions, especially in logistics and healthcare:
6.1. Warehouse ARM
The standard warehouse robotics, built to support the logistics and warehouse management. Their main objectives are transporting materials, products, by-products, sort items, and managing inventory, reducing the need for manual labor and increasing cost efficiency.
Learn more about AMR in warehouse facility on this article: AMR Warehouse: A Cost-Effective Solution for Businesses 2025

6.2. Healthcare AMR
AMR model use in health care centers and hospitals by performing tasks such as disinfection, medication delivery, and sanitation. These robots are helping to address the ongoing issue of staff shortages in the medical field, where hospitals often struggle with inadequate personnel, particularly doctors and nurses.
Additionally, AMR are less susceptible to harm from bacteria, viruses, or diseases that are common in healthcare environments. Unlike human staff who may be exposed to harmful pathogens, robots can safely operate in potentially contaminated areas without the risk of infection.
Aside from those, AMR robots are tested in different fields, such as agriculture and retail. Though those AMR application is still new and under testing, we expect that automobile robots will be far advanced in the future and become the new standard of automation.
7. The Future of AMR robots
The trajectory of Autonomous Mobile Robot points toward a transformative era of smarter, more ubiquitous automation. As industries increasingly rely on these robots to meet rising demands for efficiency and adaptability, advancements in technology and market dynamics are poised to expand their capabilities and reach. The future of AMR promises not only enhanced performance but also broader applications, reshaping how businesses operate across diverse sectors.
Advancements in AI and Robotics
Smarter AI and better sensors will push the AMR robot to predict issues, collaborate in fleets, and tackle complex environments like outdoor sites. Future models will likely feature improved decision-making abilities, powered by more advanced AI algorithms that enable real-time analysis of complex environments.
Market Trends
The AMR market is on a steep upward trajectory, driven by growing demand for automation amid labor shortages and rising operational costs. Now, with “big names” like Amazon, Samsung, Google are investing in automation technology, AMR robots are set to dominate logistics, manufacturing, and emerging fields like mining, fueled by 5G and falling costs.
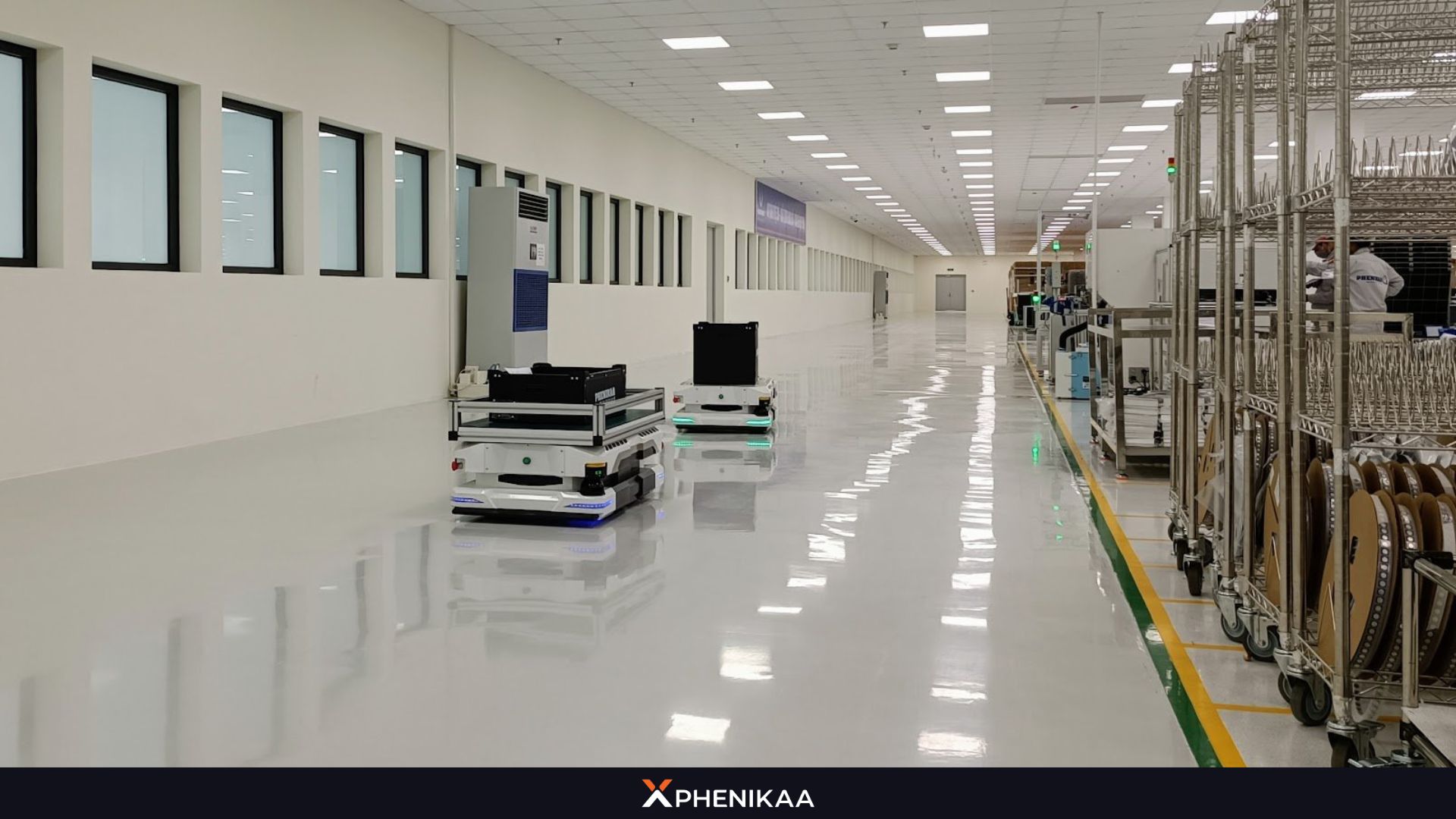

Potential for New Industries
AMRs are poised to revolutionize industries that have yet to fully embrace automation, unlocking new possibilities. For example:
- In construction: AMR could transport materials across rugged sites or assist with inventory management in real time, improving project timelines and safety
- Agriculture: The autonomous robot offers another frontier—AMRs equipped with specialized tools could autonomously plant, monitor crops, or transport harvests, addressing labor shortages and boosting precision farming.
- Hospitality: AMRs evolve beyond basic delivery roles into dynamic assistants, managing inventory or guiding guests in hotels and event spaces
Sustainability
Looking ahead, AMR robot will play a growing role in sustainable operations. Energy-efficient designs, powered by advanced batteries or renewable sources, could reduce the carbon footprint of industrial processes. With such traits, AMR robots will cut waste and emissions, though workforce shifts will demand new skills in robotics.
As they become smarter, cheaper, and more versatile, AMR will transition from specialized tools to essential partners, driving innovation and efficiency on a global scale. Businesses that invest in this technology now stand to gain a competitive edge in an increasingly automated world.
8. FAQs about AMR
- How much does AMR cost?
The cost of Autonomous Mobile Robots varies widely based on their features, complexity, and intended applications. Prices typically range from $20,000 for basic models, to $100,000 or more for advanced units with AI and better detection systems.
You can check full detail about the cost of implementing AMR into you facility in this article Autonomous Vehicle Robot Prices. The article was made by Phenikaa-X market researcher to help you easier to measure all fees related to AMR installation.
- What industries can benefit from AMR robot?
AMR robots are versatile and can be used in industries such as manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, agriculture, hospitality, and retail.
- Are AMRs safe to work alongside humans?
Yes, AMR is designed with safety features like collision avoidance and sensors to ensure safe interactions with humans.
- How do I maintain an AMR?
Regular maintenance includes software updates, sensor calibration, and battery checks. Most AMR providers offer maintenance services and support.
Conclusion
Autonomous Mobile Robots are transforming industries by enhancing efficiency, improving safety, and reducing costs. As technology continues to advance, the potential applications for AMRs are virtually limitless. Businesses that adopt AMRs today will be better positioned to thrive in the future of automation.
Phenikaa-X is one of the best AMR and robotic solutions providers. Contact us today to learn more about integrating AMRs into your business:
- Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/phenikaa.x
- Hotline: (+84) 904530545
- Email: contact@phenikaa-x.com

